First Hospital in the State to Successfully Deploy the Ranger Drug Coated Balloon™
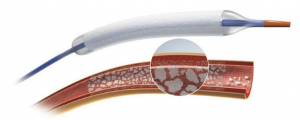
MISSOURI DELTA MEDICAL CENTER HAS BECOME THE FIRST HOSPITAL IN THE STATE OF MISSOURI TO SUCCESSFULLY DEPLOY THE BOSTON SCIENTIFIC RANGER DRUG COATED BALLOON™
SIKESTON, MO, December 15, 2020: Missouri Delta Medical Center now offers the Boston Scientific Ranger drug coated balloon (DCB), which was developed for the treatment of patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and proximal popliteal artery (PPA). The newly US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Ranger DCB provides physicians with a safe and effective option to treat PAD, which impacts more than 8.5 million American adults. It is a common circulatory problem in which atherosclerosis builds and narrows arteries, consequently reducing blood flow to limbs. It is estimated that 12 to 14% of the general population is affected by PAD. The Ranger DCB was designed with a very low dose of drug and a proprietary coding, which efficiently transfers drug into the tissue, resulting in high primary patency rates and low systemic drug exposure for patients. The low-profile platform of the balloon also assists clinicians in performing streamlined procedures and navigating through challenging anatomy in order to deliver consistent therapy. The first patient implant at Missouri Delta Medical Center was performed on December 10, 2020 by cardiothoracic surgeon, Dr. Paula Guinnip. She stated that, “Improvements in patency were a real benefit in considering the use of this effective balloon.” Clinical trial results have demonstrated the Ranger DCB’s safety and efficacy versus standard percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with 12 month freedom from major adverse events (MAE) being 94.1% for those treated with Ranger DCB versus 83.5% for standard PTA and 12 month-binary primary patency- a measure of the target vessel remaining unobstructed- was 82.9% for the Ranger DCB and 66.3% for standard PTA. The COMPARE trial is the world’s first head to head randomized controlled trial
(RCT) comparing low-dose Ranger to a higher dose as studied in the IN.PACT trial. Ranger demonstrated similar primary patency as IN.PACT, with a significantly lower drug dose density. The company announced CE Mark for Ranger DCB in 2014 and the FDA granted regulatory approval on November 2, 2020. For more information on the Ranger DCB, visit https://www.boston scientific.com/en-US/medical-specialties/vascular-surgery/drug-eluting therapies/ranger.html.
